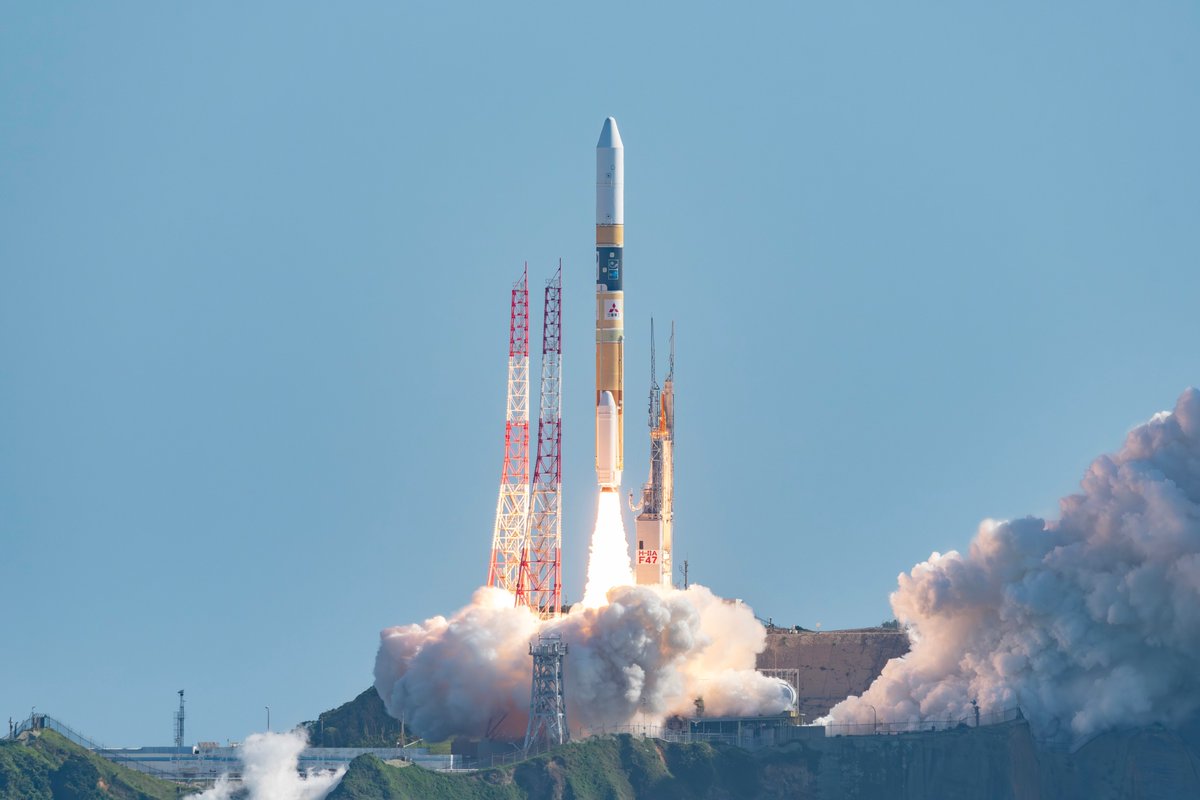

H-IIA 202 | GOSAT-GW
Programma
Pad
The Tanegashima Space Center is the largest rocket-launch complex in Japan. It is located on the southeastern tip of Tanegashima, an island located south of Kyushu, an island and region and Japan. It was established in 1969 when the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) was formed, and is now run by JAXA. The activities that take place at TNSC include assembly, testing, launching, and tracking satellites, as well as rocket engine firing tests.
Rocket

H-IIA (H2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The liquid-fueled H-IIA rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit, to launch a lunar orbiting spacecraft, and to launch Akatsuki, which studied the planet Venus. Launches occur at the Tanegashima Space Center.
Full Name: H-IIA 202
Maiden Flight: 2001-08-29
Total Launch Count: 34
Successful Launches: 34
Failed Launches: 0
Mission
Mission Name: GOSAT-GW
Type: Earth Science
Description: GOSAT-GW (Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite Greenhouse gases and Water cycle), formerly known as GOSAT 3, is JAXA's next generation satellite to monitor the greenhosue gases like carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. It is the follow on to the GOSAT 2 (Ibuki 2) and GCOM-W (Shizuku) missions. GOSAT-GW will have two missions: greenhouse gases observation for Japan's Ministry of the Environment and the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), and water-cycle observation for JAXA. By developing the GOSAT-GW satellite, Mitsubishi Electric will contribute to measures for preventing disasters attributed to global warming and climate change, and to advance scientific and technological methods that enable more accurate prediction of climate change. In December 2013, Mitsubishi Electric (MELCO) was selected as the prime contractor for the spacecraft and the instruments.
Orbit: Sun-Synchronous Orbit
Updates

Cosmic_Penguin
2025-04-23T04:59:00ZNET June 23 UTC/early morning June 24 JST.

Cosmic_Penguin
2024-12-09T10:56:00ZNET Q2 due to satellite testing delays.


Cosmic_Penguin
2025-03-18T21:28:00ZNET June 2025.

Cosmic_Penguin
2024-01-09T14:26:07ZTweaked approximate launch date per launch manifest (P.129 of source).