
Falcon Heavy | Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
Programma
Pad
The John F. Kennedy Space Center, located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of NASA's ten field centers. Since 1968, KSC has been NASA's primary launch center of American spaceflight, research, and technology. Launch operations for the Apollo, Skylab and Space Shuttle programs were carried out from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 and managed by KSC. Located on the east coast of Florida, KSC is adjacent to Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS).
Rocket
![[AUTO] Falcon Heavy - image](https://thespacedevs-dev.nyc3.digitaloceanspaces.com/media/images/falcon_heavy_image_20220129192819.jpeg)
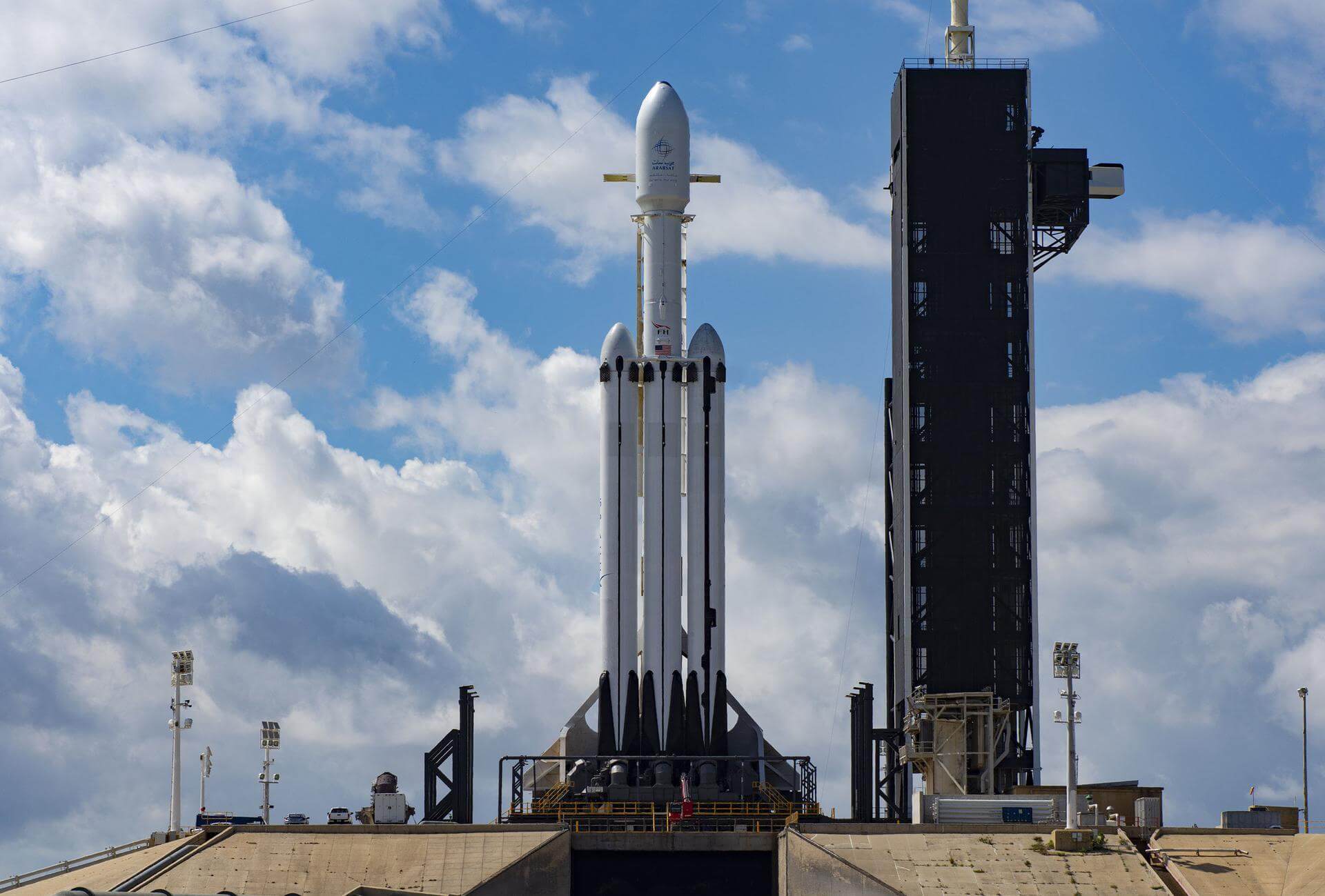
The Falcon Heavy is a variant of the Falcon 9 full thrust launch vehicle and consists of a standard Falcon 9 rocket core, with two additional boosters derived from the Falcon 9 first stage.
Full Name: Falcon Heavy
Maiden Flight: 2018-02-06
Total Launch Count: 11
Successful Launches: 11
Failed Launches: 0
Mission
Mission Name: Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
Type: Astrophysics
Description: The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is a NASA infrared space telescope with a 2.4 m (7.9 ft) wide field of view primary mirror and two scientific instruments. The Wide-Field Instrument (WFI) is a 300.8-megapixel multi-band visible and near-infrared camera, providing a sharpness of images comparable to that achieved by the Hubble Space Telescope over a 0.28 square degree field of view, 100 times larger than imaging cameras on the Hubble. The Coronagraphic Instrument (CGI) is a high-contrast, small field of view camera and spectrometer covering visible and near-infrared wavelengths using novel starlight-suppression technology. Roman objectives include a search for extra-solar planets using gravitational microlensing, and probing the expansion history of the Universe and the growth of cosmic structure, with the goal of measuring the effects of dark energy, the consistency of general relativity, and the curvature of spacetime.
Orbit: Sun-Earth L2
Updates

Nosu
2022-07-20T07:04:29ZAdding launch NET October 2026