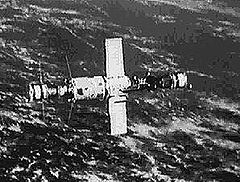
Salyut 6
Fondazione: 1977-09-29
Salyut 6, also known as DOS-5, was a Soviet orbital space station, the eighth flown as part of the Salyut programme. Launched on 29 September 1977 by a Proton rocket, the station was the first of the "second-generation" type of space station. Salyut 6 possessed several revolutionary advances over the earlier Soviet space stations, which it nevertheless resembled in overall design. These included the addition of a second docking port, a new main propulsion system and the station's primary scientific instrument, the BST-1M multispectral telescope. The addition of the second docking port made crew handovers and station resupply by unmanned Progress freighters possible for the first time.

Salyut 7
Fondazione: 1982-04-19
Salyut 7, (a.k.a. DOS-6) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first manned in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including 12 manned and 15 unmanned launches in total. Supporting spacecraft included the Soyuz T, Progress, and TKS spacecraft.

Genesis I
Fondazione: 2006-07-12
Genesis I is the first of two experimental inflatable space habitats. It is a one-third scale model of Bigelow Aerospace's BA330 Module.

Genesis II
Fondazione: 2007-06-28
Genesis II is the second of two experimental inflatable space habitats. It is a one-third scale model of Bigelow Aerospace's BA330 Module. Genesis II became inactive after the avionics systems stopped working 2.5 years into it's lifetime.
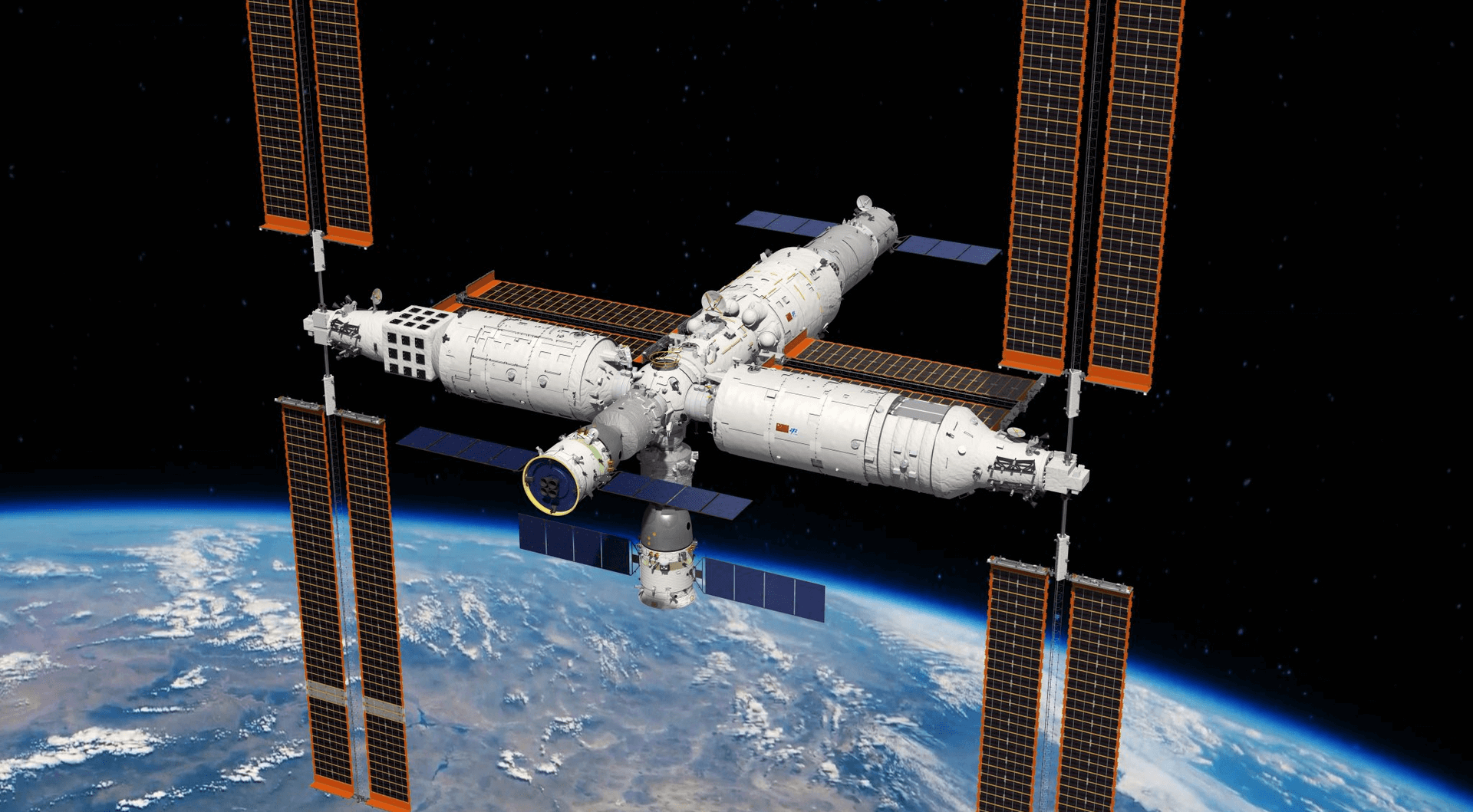
Tiangong space station
Fondazione: 2021-04-29
The Tiangong space station is a space station placed in Low Earth orbit between 340 and 450 km above the surface. It will be roughly one-fifth the mass of the International Space Station and about the size of the Mir space station.